Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Wednesday, 2 April 2025 13:41 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 In a world where uncertainty is progressively becoming the new normal, economic crises are also becoming increasingly prevalent regardless of the cause of the crisis. During such economic downturns, countries deploy various policy tools and risk mitigating actions. These tools and actions are predominantly context and time specific, aiming to stabilizing the economies.
In a world where uncertainty is progressively becoming the new normal, economic crises are also becoming increasingly prevalent regardless of the cause of the crisis. During such economic downturns, countries deploy various policy tools and risk mitigating actions. These tools and actions are predominantly context and time specific, aiming to stabilizing the economies.
Among these tools, international reserves stand out as one of the most crucial buffers, playing an indispensable role in maintaining confidence and stability during a crisis. Although there is a theoretical norm stating that the level of reserves required to be maintained under a flexible exchange rate policy could be comparatively lower, countries have increasingly accumulated their reserves as a buffer against the exogenous shocks as they have become a common paradigm.
International Reserves
International reserves are defined as external assets which are readily available and controlled by the monetary authorities and the central banks as a safeguard for ensuring that the country can meet balance of payments financing needs, external debt obligations, and smooth out fluctuations of the domestic currency (IMF, 2025). These external assets include foreign currencies, fixed income securities, gold, special drawing rights and other reserve assets.
International Reserves as a Shield against Turbulences
Currency stabilization: During a crisis, one of the first casualties is often the country’s local currency. It can experience sharp fluctuations due to uncertainty and probable capital outflows, eroding investor confidence, or creating inflationary pressures. A robust level of international reserves offers the capacity for a central bank to make timely interventions and curtail exchange rate volatility, thereby preventing the local currency being exposed to unwarranted fluctuations.
Debt repayment and external obligations: In a crisis, a mandatory challenge for a country is financing its external debt obligations without any lapses. Therefore, having an adequate buffer of international reserves is the comfort factor in ensuring the country’s ability to service external obligations.
Boosting investor confidence: The presence of a substantial international reserve signifies to the international market and to potential investors that the country is geared to weather any storm. In times of economic uncertainty, investors seek safe havens. A robust level of international reserves reflects and reassures the government’s ability to handle immediate shocks, thereby creating positive outcomes including capital inflows.
Access to international financial assistance: During periods of crisis, countries in distress negotiate for various mechanisms such as seeking assistance from multilateral organisations such as IMF, World Bank and ADB as well as from friendly governments and central banks in exchange for a promise to repay with reserves in the future. In such a context, at least a bare minimum level of international reserves with a gradual flow of impending inflows would be a definite necessity.
Supporting trade and import stability: Global crises often disrupt global trade flows, causing volatility in the prices of imported goods and commodities. At the same time, crises which can erupt within the countries can experience severe strain on their international reserve positions, worsening the country’s ability to import the essential commodities, i.e fuel, coal, cooking gas, medicines and food items. Having a sufficient buffer of international reserves in such circumstances would place the country in a better position to maintain economic stability, at least at a manageable level.
Sri Lanka: The tale of Multiple Challenges
The Sri Lankan economy had its strongest blow since 2020 onwards, with a series of unprecedented events occurred both globally and locally, affecting the key sources of foreign currency inflows to the country. The economy contracted severely, and inflation soared to record highs whilst the usable international reserves dwindled sharply, requiring the government to announce a debt standstill in April 2022.
At this stage, the most challenging tasks laid ahead of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka were to tackle the rapidly rising inflation with a carefully managed exchange rate and the building of international reserves. Hence, the subsequent policy initiatives alongside the timely assistance of the IMF led the external sector to show some resilience, thereby opening avenues to accumulate reserves gradually. These moves helped the economy to come out of the crisis slowly, whilst domestic and external debt restructuring programs were successfully concluded. The continuous purchases of US dollars from the domestic forex market to build up reserves mainly from non-debt creating flows led to gross official reserves surpassing US dollars 6 billion by October 2024. Although the way ahead is longer, prudent, crisis specific, and timely economic measures enacted, allowed the country to run through the most turbulent years in the Sri Lankan history since Independence, in a commendable manner.
Graph 1: Gross Official Reserves (GOR) and GOR excluding PBoC Swap from 2020-2025
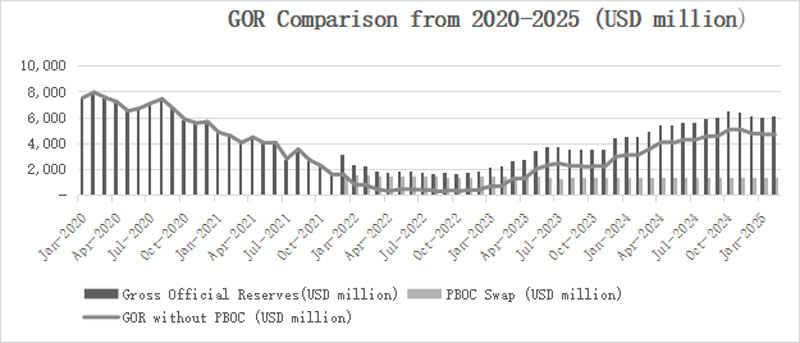
Source: Central Bank of Sri Lanka
International Reserve Management
Official international reserves of the country are managed by the Central Bank through a careful balance among liquidity, safety and return. Hence, the Central Bank manages its reserves in accordance with a scientific model known as the Strategic Asset Allocation framework, which aligns with the asset and liability structure of the Central Bank and the Government. The said framework mainly considers the objectives of liquidity requirements, capital preservation, income generation and the overall risk tolerance of the Central Bank. Therefore, the adoption of appropriate reserve management policies concerning the asset composition, currency composition, investment instruments, and acceptable duration targets of the reserves portfolio would primarily depend on the country's specific foreign currency requirements, external debt liabilities, impending inflows, policy settings and external circumstances.
Insights into Official International Reserves
Although a country receives foreign currency inflows on a continuous basis through sources such as exports, remittances and capital inflows etc, such inflows do not constitute a part of the official international reserves until the Central Bank purchases excess liquidity from the recipient banks. Once purchased, those foreign currencies would be a part of the official international reserves, and the central bank is mandated to manage them prudently. Alternatively, the Central Bank could supply the reserves to curtail the undue volatility of the local currency and deploy for settling foreign currency debt obligations. The recipients of those reserves supplied, i.e the banks, may utilize the foreign currencies for day-to-day transactions including import financing. Hence, it is important to understand that official international reserves are not readily and directly available for import financing. Meanwhile, despite the common belief that having a very large reserve is a necessity, it may not be the best option at times, as there are limits to the amount of reserves a country should accumulate. Whilst having too little reserves can leave a country vulnerable to external shocks, maintaining an excessive reserve could also be costly.
In conclusion, international reserves act as an economic lifeline during crises. The modern role of international reserves is not merely confined to stabilizing the currency and boosting investor confidence but provides the necessary liquidity for external debt obligations and pathway to economic and social stability. For a country facing economic volatility, the international reserve position goes beyond a strengthened balance sheet and stands out as the power of resilience.
References
Official Reserve Assets and Other Foreign Currency Assets, IMF, 2025
CBSL weekly and monthly economic indicators
José De Gregorio De J and Tokman R.A, 2024, Flexible exchange rate regime and forex intervention, BIS working paper