Saturday Feb 21, 2026
Saturday Feb 21, 2026
Thursday, 12 December 2019 03:06 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
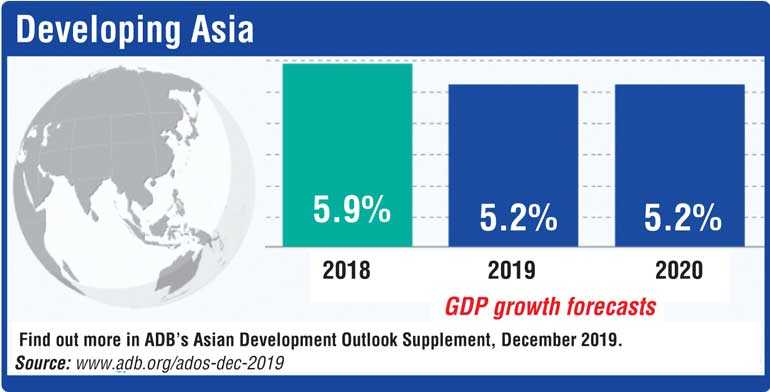
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has trimmed its forecasts for economic growth in developing Asia this year and next year as growth in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) and India is weighed down by both external and domestic factors.
In a supplement to its Asian Development Outlook 2019 Update released in September, ADB now expects gross domestic product (GDP) in the region to expand 5.2% in both 2019 and 2020, down from the September forecast of 5.4% growth this year and 5.5% next year.
“While growth rates are still solid in developing Asia, persistent trade tensions have taken a toll on the region and are still the biggest risk to the longer-term economic outlook. Domestic investment is also weakening in many countries, as business sentiment has declined,” said ADB Chief Economist Yasuyuki Sawada. “Inflation, on the other hand, is ticking up on the back of higher food prices, as African swine fever has raised pork prices significantly.”
The supplement forecasts inflation of 2.8% in 2019 and 3.1% in 2020, up from the September prediction that prices would rise 2.7% this year and next.
In East Asia, growth in the PRC is now expected at 6.1% this year and 5.8% next year due to trade tensions and a slowdown in global activity coupled with weaker domestic demand, with family wallets being hit by pork prices that have doubled relative to a year ago. Growth could accelerate, however, should the United States and the PRC come to an agreement on trade, the report says. In September, ADB forecast GDP growth of 6.2% in 2019 and 6.0% in 2020.
Hong Kong, China, already in technical recession, will see severe downward pressures persist possibly into 2020. The economy is now expected to contract 1.2% this year and grow 0.3% next year.
In South Asia, India’s growth is now seen at a slower 5.1% in fiscal year 2019 as the foundering of a major nonbanking financial company in 2018 led to a rise in risk aversion in the financial sector and a credit crunch. Also, consumption was affected by slow job growth and rural distress aggravated by a poor harvest. Growth should pick up to 6.5% in fiscal year 2020 with supportive policies. In September, ADB forecast India’s GDP to grow 6.5% in 2019 and 7.2% in 2020.
In Southeast Asia, many countries are seeing continued export declines and weaker investment, and growth forecasts have been downgraded for Singapore and Thailand. GDP growth is expected to slow in the Pacific with activity in Fiji, the subregion’s second largest economy after Papua New Guinea, expected to be more subdued than previously anticipated.
Central Asia is the only subregion where prospects look a little brighter now than in September, largely thanks to increased public spending in Kazakhstan, the region’s largest economy. Central Asia is now forecast to grow 4.6% in 2019, up from the previous prediction for expansion of 4.4%. The forecast for 2020 is for growth of 4.5%. Kazakhstan’s economy is seen expanding by 4.1% this year and 3.8% next year.
ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty. In 2018, it made commitments of new loans and grants amounting to $21.6 billion. Established in 1966, it is owned by 68 members—49 from the region.