Sunday Feb 15, 2026
Sunday Feb 15, 2026
Thursday, 24 February 2022 00:00 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}

Preamble
Environment is a globally interconnected natural network. All activities and events on the environment have consequences or impacts on environment and lead to Global Warming (GW) and Climate Change; I would say they are products of such activities carried out by humans as well as natural calamities.
Change; I would say they are products of such activities carried out by humans as well as natural calamities.
The effects of Green House Gases (GHG) have been assessed successfully linked to climate change with computer aided modelling and data collected over the years to prove the excess earth surface temperature was a result of reflection of heat back to the earth surface from GHG in the atmosphere and causing climate change viz: ice melting, rising sea levels and irregulars weather patterns, etc. The measurements that were taken have shown a temperature rise of the earth surface in the last 40 years which substantiate the argument of change of climate.
The major contributor of GHG has been determined as carbon and reduction of carbon was the key agenda and a major concern being discussed in COP26s (Conference of the Parties). As the generation of power, electricity was primarily produced by fossils fuels, the transition to renewable sources is paramount importance to reduce GHG. Although, the transition to wind and solar are considered as available options, wind and solar are characterised on seasonal and time variations. As the case may be, careful assessment is needed before deciding on the options and adoption of renewables to a level 70% to 80% and also implementation timeframe.
The Carbon Tax and Emission Trading Schemes that are being implemented need to be refined and should be integratable across the continents, countries and industries that are at various stages of development and growth.
Climate change sceptics on the other hand reject all the ascensions and predictions and challenge the modelling and data used are incorrect. We have witnessed the consequences of wrong decisions taken by many administrations in the past hitherto.
This paper discusses the climate change, its effects and current schemes in place to mitigate harmful consequences as a results of Green House Gases (GHG) emissions that lead to Global Warming (GW) creating an imbalance to the ECO System.
Green House Gases
Green House Gas (GHG), any gas that has the property to absorb thermal infrared radiation emitted from earth surface and reradiating back to earth surface is classified as GHG. The gases that fall into GHG classification are, Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Water Vapour (H2O) Nitrous oxide (N2O) and Industrial gases such as Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) Perfluorocarbons (PFCs) Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). Out of the above list, CO2, CH4 and Water Vapour (H2O) are the predominant components that contribute to Green House Effect.
Green House Effect
Some of the infrared radiation passes through the atmosphere but most are absorbed and re-radiated by GHG molecules and clouds. This is called Green House Effect and result warming the earth surface and the lower atmosphere. As long as the there is more and uncontrollable GHGs in atmosphere, the re-radiation and scattering of infrared radiation back to earth causes excessive rise in temperature which is beyond to sustain a balanced and healthy ECO system.
Sources of GHG
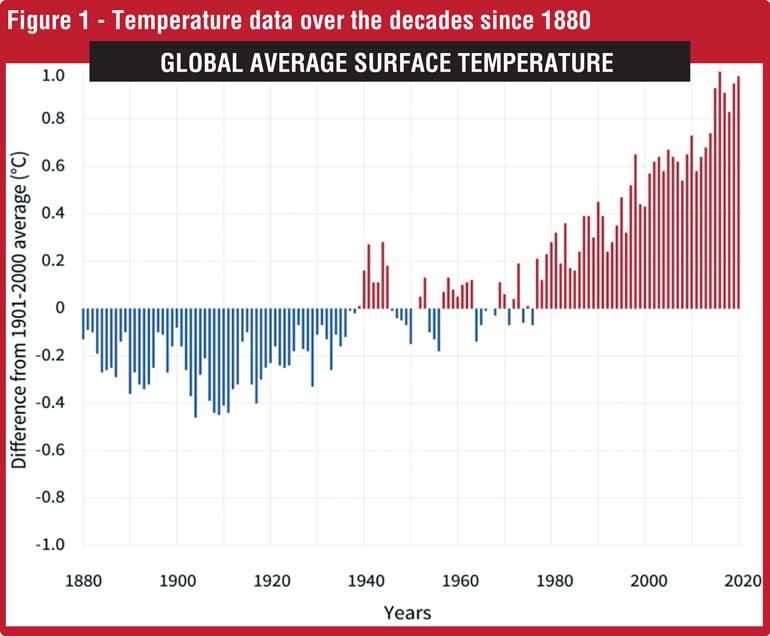
To put into perspective, there are several sources that emit GHG, global fossil fuel emissions mostly by humans, wildfires, land and submarine volcanos and non-volcanic escapes of CO2–CH4 from the upper mantle of earth (from carbon bearing rocks) are natural occurrences. The wildfires contribute 22% of global fossil fuels and land volcanic less than 1% as opposed to submarine volcanos which produces vastly greater amounts. To further compare in terms of absolute volumes, CO2 emissions has risen from near zero in year 1750 to 35 Gigatons in year 2020 thus adding concentration from 280 to 420 ppm (parts per million) in the same period. (Refer Figure 1):
Global Warming (GW)
To date the scientific modelling had revealed, the excessive GW has destructive consequences to the ECO system in terms of droughts, floods as a result of unforeseen rain patterns, melting of iceberg and rising sea levels. To elevate from such destructions, the primary focus was to reduce the GHGs and advocate the participation of all nations in the mitigation process. The climate change believers have been active for the past decades propagating and promoting collaborative effort amongst nations, at the same time sceptics have been advocating it is a manmade hoax.
Out of the climate change activists, it has come to light that majority have multiple agendas and motives. Some of them, including academia, are promoting Solar (PV) energy as a renewable source of energy whom are driven by multinational agencies for getting handsome grants for research and marketing. A former vice President of US travelling across the countries with a private jet burning billions of carbons promoting the cause of carbon neutrality. This was the hypocrisy of some of the activists, one must also access how much of carbon emits in manufacturing PV solar panels and also to destroy/recycle upon reaching the lifespan.
Quoting another known example where the former Australian Climate Change Head as a result of his modelling recommended desalination plant for New South Wales Australia, predicting long drought and water scarcity in the future. Based on the recommendation the State Government built a desalination plant and now being run idle and paying only for maintenance.
These events, happened in past and ongoing basis provide ammunition to sceptics to attack the activist and discredit the prediction of scientific modelling. They also argue that the motives are primarily driven by business and commercial benefits.
Mitigation of global warming
Mitigation of global warming is complex and monumental tasks to bring all nation to agree on. The difficulty as I see is that, not all nations are equally developed and economically strong. Therefore, it is vital to make an integrated plan, not equal but to cater the needs of individual nations understanding the ground realities. Before one embark on mass scale rollout, few inexpensive programs need to be introduced and make compulsory, example LED lighting as opposed to incandescent lights which has long life span, harvesting rainwater for domestic usage, deploying smart electricity (KWh) meters to spread the load across peak, off-peak and shoulder where households benefit reducing the monthly bill instead of flat metering, encourage peri-urban living as opposed to city and urban, encourage construction of carbon neutral home limiting the use of cement and bricks, use of biogas, etc.
Carbon trading
Determining a price for carbon has been opined as a mechanism to reduce the carbon emission, also as an effective way to galvanise adaptation of clean technology globally, although it somewhat lacks strong conviction and direction. Since the establishment of very first Emission Trading System (ETS) system in year 2005 by European Union, similar ETS have come to existence in various regions. Nonetheless, the face value of ETSs is encouraging they lack vitality. Recently, China introduced its domestic ETS covering 30% of GHG emissions and significantly was the world largest scheme as reported. However, it was envisaged that it is beneficial to build a global emission integrated framework rather than operating individual domestic ETSs in tackling the climate change where nations could exchange their carbon credits efficiently. The integration facilitates countries to decarbonise faster with most effective pricing mechanism.
Integrated framework for ETS
Integrated framework is a necessity to bring all nations to one scheme and make the big polluters to reduce the carbon emissions encouraging them to invest in abating measures to reduce their emissions. The scheme is to target cost effective means of investing on improved processes to achieve clean fuel as opposed to paying significant tax for the carbon they emit. Furthermore, to exchange credits between nations will ease developing and underdeveloped economies to continue the development efforts unabated but with some conditions.
To illustrate the European Union ETS, it is based on principle of ‘Cap and Trade’. It sets an absolute limit or ‘Cap’ on the total amount of certain greenhouse gases that can be emitted each year by the entities covered by the system, and the ‘Trade’ is a market for companies to buy and or sell allowances they gained or lost, allowing the price of carbon to be determined by supply and demand on a free market setting. Trading gives companies a strong incentive to save money by cutting emissions in the most cost-effective ways.
To summarise and put in context the current status, only 4/5th of the emissions isn’t capped or priced. The average price of carbon tonne is $ 3 and a small percentage approx. 3.8% are priced at $ 40 per tonne, a significant disparity. Yet again more countries are reluctant and resistive to accept such schemes in fear of cost of business and damaging the economic growth. This is a colossal task of COP to bring all nation leaders together and with consensus design an implementable scheme and monitor and measure what they emit irrespective of boundaries.
Carbon leakage risk is a key factor that to be addressed in the ETS trading scheme preventing big polluters moving offshore seeking tax heavens where the carbon ‘Cap’ is high. Instead of addressing industry by industry, it was said the leakage should be prevented from the power sector rather than polluters, e.g. steel industry.
Current status of Carbon Reduction Program
Countries have been grouped as follows to identify the current status of implementation of the Carbon Reduction Program. The two main ones are ETS and Fixed price (a tax) of Carbon. Some countries adopt a hybrid solution having both options. The categories are listed from A to G:
A. ETS implemented or scheduled to be implemented
B. Carbon tax implemented or scheduled to be implemented
C. ETS and Carbon tax under consideration
D. ETS and carbon tax implemented or scheduled
E. Carbon tax implemented or scheduled, ETS under consideration
F. ETS implemented or scheduled, ETS or carbon tax under consideration
G. Either ETS or carbon tax implemented or scheduled
[Refer figure opening the following URL (of 7 July 2021 prepared by World.org)
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/35620/9781464817281%20Executive%20Summary.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y (Refer page 6/12).]
On analysing the world map of the carbon reduction program, China falls under category A, focussing on ETS. In Canada and in European bloc, they fall to category D with hybrid implementation. Argentina, Northwest territories and South Africa fall in B having Carbon Tax schemes. Several countries, namely, Brazil, Turkey, Pakistan, South East Asian bloc, where the Carbon Tax scheme is under consideration. Russia, Australia, Middle East, Sub Continent, Africa and US have not firmly committed to either A or B.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, ETS scheme carbon price is set by market for carbon emitted over the Cap. Cap should be designed based on the local conditions of individual countries so that not to affect badly on growth in economy. As previously said, part of the revenue earned to be used to compensate the households and also for consumer as a result of increased pricing. Over time, the ‘CAP’ to be reviewed and to finally achieving zero carbon emissions, targeted year 2050.
As opposed to ETS, some jurisdiction, governments impose a fixed tax for Carbon Tonne the individual or group of businesses emit. Both these schemes encourage companies to cut emissions of harmful greenhouse gases and encourage to reduce their operating costs by way of improved processes and practices through innovations. As all the countries haven’t the same capabilities to improve processes, it is necessary to transfer technological innovations in a favourable cost-effective means. Such arrangements will enable a sustainable growth in reduction of carbon without aberrant.
At a time, Sri Lanka is grappling with acute macroeconomic crisis which spurts to every facet of life of her citizens, announcing Sri Lanka’s ambitious plan to implement of COP26 recommendation is only a rhetorical and unsustainable. The opportunistic, ill-timed alignment to COP26 has hidden agendas to lift the image of Sri Lanka and its Government which has been badly damaged in many fronts and subjected to criticism locally and internationally.
Finally, whatever the scheme is implemented it is important to measure, monitor and regulate, otherwise all the efforts will be wasted. Therefore, a robust monitoring and regulatory systems are needed to derive the benefits and should be incorporated in COP26 for either carbon tax or ETS.
Citations:
[1] https://www.britannica.com/science/greenhouse-gas
[2] https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-global-temperature
[3] https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/climatescience/greenhousegases.html
[4] https://www.google.com/search?q=greenhouse+gases&rlz=1C1GIVB_enAU788AU788&sxsrf=APq-WBsACyKe8UiEl5aGJR-e1tRtIj7_9w:1644209166097&tbm=isch&source=iu&ictx=1&vet=1&fir=RzBFN9mJkutIZM%252Ck1-Psx4w2WnatM%252C_%253BjK7Tp7S8C_PhRM%252C1ZrLFBmRqd-vwM%252C_%253BphrPL2jHzMHMMM%252C27Ov-QCUeywO8M%252C_&usg=AI4_-kQ31wj0wcGsqqRN9qf07bNYr8-cYg&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiB45-65Oz1AhW7TmwGHcYiArUQ_h16BAgGEAE&biw=1920&bih=1009&dpr=1#imgrc=jK7Tp7S8C_PhRM&imgdii=Id3ETgISEu30bM
[5] https://www.edf.org/climate/how-cap-and-trade-works
[6] https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/35620/9781464817281%20Executive%20Summary.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y