Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday Feb 19, 2026
Thursday, 7 April 2022 00:23 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 By Kushan Kumarasiri
By Kushan Kumarasiri
Digital economy
We have seen the advent of online business platforms like e-commerce and digital banking in recent years and now even other traditional sectors like agriculture and manufacturing are slowly becoming tech-orientated. An economy generated from borderless, online connections of people, business, data, processes and more is termed a digital economy. It is also referred to by many as the web economy, internet economy or even new economy.
Since business has and is still undergoing a digital transformation, there is a hyper-connectivity between people, organisations and machines. Internet, mobile technology and the internet of things (IoT) have impacted the way trade is carried out and thus have transformed the global economy too.
The digital economy plays a pivotal role in shaping the business world as it encourages the adoption of newer technologies that streamline operations, thus helping to promote a more efficient execution of tasks. Companies participating in the rapidly developing digital asset ecosystem are enabling a new era of global online trust that, in turn, is creating utility for consumers, reshaping business modules, recognising competitive dynamics and redistributing value across industries. Innovative “pick and shovel” companies are seeking to capitalise on secular growth trends, extending well beyond the digital asset ecosystem, which ultimately presents new, exciting opportunities for investors. The digital asset segment of the digital economy rose as high as ~$ 3 trillion in total market value* over the course of 2021.
|
iBank-UK Chief Executive Officer and Colombo Block Exchange Founding Chairman Dr. Shiva Narayan
|
Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
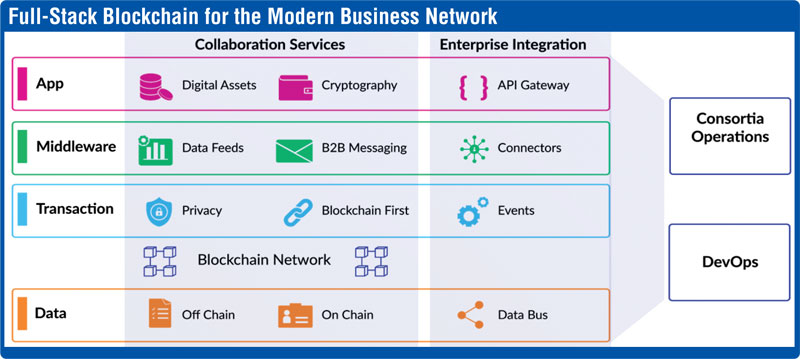
In past years, the digital assets and cryptocurrency industry has evolved rapidly in many countries around the globe. Institutions have begun facilitating the purchase and sale of cryptocurrencies, offering custody services and are now looking forward to get involved in “Decentralised Finance (DeFi)”. The existing growth in DeFi is driven by digital native firms, venture capitalists and individuals. The entry of traditional institutions into DeFi will be a significant milestone in the industry’s maturation and progress towards widespread adoption. It will have impacts on the broader financial system and existing forms of financial intermediation.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) is intended to transform the current centralised global financial infrastructure into an internet-based decentralised model that relies on open-source protocols instead of traditional financial intermediaries. This new concept presents traditional financial institutions with a series of opportunities to grow by enhancing the existing operations and services.
Why it is important?
If you apply this decentralised peer-to-peer model on a global basis to the various forms of financial transactions that require an intermediary today (for example, collateralised lending, interest-bearing deposits or investment portfolio management), the potential impacts to the existing global financial system and its intermediaries become significant.
Ways that Decentralise Finance applications could change the traditional process and parties involved:
What exchanges do?
The exchanges can send cryptocurrency to a user’s personal cryptocurrency wallet. Some can convert digital currency balances into anonymous prepaid cards which can be used to withdraw funds from ATMs worldwide while other digital currencies are backed by real-world commodities such as gold. The creators of digital currencies are often independent of the digital currency exchange that facilitates trading in the currency. In one type of system, digital currency providers (DCP) are businesses that keep and administer accounts for their customers, but generally do not issue digital currency to those customers directly. Customers buy or sell digital currency from digital currency exchanges, who transfer the digital currency into or out of the customer’s DCP account. Some exchanges are subsidiaries of DCP, but many are legally independent businesses. The denomination of funds kept in DCP accounts may be of a real or fictitious currency.
Does Sri Lanka need an exchange?
Just like many individuals in other countries around the globe, Sri Lankans are also involved in Crypto trading at different scales for past many years even though there have been no legitimate grounds to bring an overall legal framework for such trading within the country. Such individual investors need to crucially evaluate where and how to transact in cryptocurrencies, and whether staking tokens that offer you.
Impact of not having a legitimate crypto exchange
What Sri Lanka needs to do
In accordance to the national policy framework, “Vistas of Prosperity and Splendour”, which highlights the importance and values of a technology-based society, Sri Lanka has now observed the necessity of developing an integrated system of digital banking where Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Mining technology has been identified to pace on par with the global partners in the region while expanding trade to the international markets.
For a progressive introduction of the Blockchain Technology, all related authorities need to capitalise on below key requirements to be fulfilled prior to implementation.
Supporting the actions taking place, iBank-UK CEO Dr. Shiva Narayan will use his years of experience and expertise in both Banking and Blockchain Technology to introduce the same to Sri Lanka as one of the key aspects of “Colombo Block Exchange Ltd.”, being its Founding Chairman.
The current economic crisis that exists in the country needs to open its doors to these kinds of groundbreaking solutions that can save the country from its current and future downturns and it is our view that Sri Lanka is still not late to join this emerging industry by making required monitoring the controlling in place to introduce “Blockchain” solutions and “Crypto Exchange” to the country.
For further information contact:
Dr. Shiva Narayan
(iBank Corporation – UK)
+44 786 100 5151
[email protected]
Kushan Kumarasiri
+94 768 913 400
[email protected]