Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Tuesday Feb 17, 2026
Monday, 13 June 2022 00:32 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
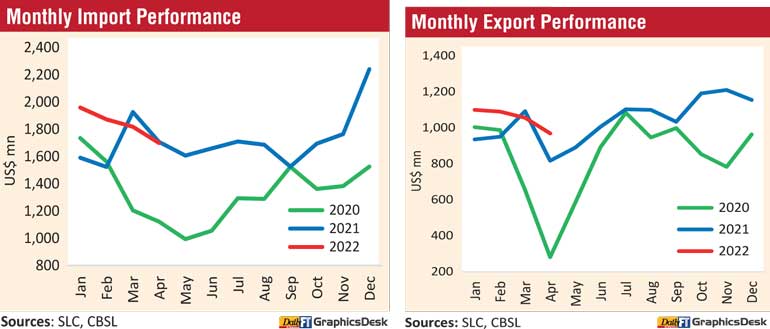
Expenditure on imports has declined, year-on-year, for the second consecutive month in April as curb measures by the Central Bank kicked in whilst higher exports helped cut the trade deficit. Imports in April amounted to $ 1.699 billion down by 0.5%. However, April data reflects a sharper dip in comparison to $ 1.8 billion spent in March.
For the first four months it was higher by 8.9% to $ 7.35 billion.
CBSL also said the trade deficit recorded a month-on-month decline for the fourth consecutive month in April 2022, supported by the policy measures that were aimed at discouraging non-urgent imports as well as higher growth in exports.
It said a decline in expenditure was observed in import of non-food consumer goods and investment goods, while an increase was recorded in import of food and intermediate goods.
The restrictions imposed by the Government on the importation of non-urgent goods and the impact of large depreciation of the exchange rate may have contributed to this decline.
Expenditure on the importation of consumer goods declined by 15.4% in April, compared to April 2021, due to the 43.4% reduction in non-food consumer goods imports.
This decline in expenditure on non-food consumer goods was broad-based, but the drop-in imports of telecommunication devices (mainly, mobile phones), home appliances (mainly, televisions), and medical and pharmaceuticals (mainly, medicaments) was notable. However, a slight increase in expenditure was recorded in clothing and accessories.
Meanwhile, the food and beverages import expenditure increased by 19.8%, led by the increase in the expenditure on milled rice imports.
Further, a sizable increase was also observed in the import expenditure of dairy products (mainly, milk powder), and vegetables (mainly, garlic and chickpeas).
Expenditure on the importation of beverages also increased to some extent (alcoholic and other beverages).
However, the import expenditure on sugar declined by 35.6% YoY in April 2022, along with oils and fats, fruits, seafood, and spices.
Intermediate goods: Expenditure on the importation of intermediate goods increased by 11.3% in April 2022, compared to a year ago, driven by imports of fuel and textile and articles.
Despite the non-importation of crude oil, the expenditure on fuel (that includes refined petroleum and coal) increased by 23.5% YoY, recording at $ 510 million due to higher average import prices.
The categories of intermediate goods that recorded an increase include agricultural inputs (mainly, animal fodder), chemical products (mainly, essential oils), plastics and articles thereof (mainly, ethylene polymers, and plastic plates and sheets), food preparations (mainly, malt extract and liquid margarine), paper and paperboard and articles thereof, mineral products, diamonds, precious stones and metals, and unmanufactured tobacco.
However, some types of intermediate goods, including fertiliser, base metals, vehicle and machinery parts, wheat, and rubber and articles thereof showed a decline.
Investment goods: Import expenditure on investment goods declined by 24.6% in April, compared to April 2021. Almost all types of goods listed under all three main investment goods categories, namely, machinery and equipment, building materials and transport equipment, recorded a decline.
Some increases in import expenditure were observed in relation to engineering equipment, articles of iron and steel, electronic equipment, and electric motors and generating sets.
Import indices: The import volume index declined by 20%, while the import unit value index increased by 24.4% YoY in April, implying that the marginal decline in import expenditure in April 2022 was mainly driven by the volume effect.
Performance of merchandise exports
Overall exports: Earnings from merchandise exports in April increased by 18.5% over April 2021, recording at $ 970 million. An increase in earnings was observed in industrial exports and agricultural exports, while a decline was recorded in mineral exports.
The cumulative export earnings increased by 11% during January-April 2022 over the same period of last year, amounting to $ 4.21 billion.
Industrial exports: Earnings from the export of industrial goods increased in April 2022 by 21.9%, compared to April 2021. A broad-based increase in earnings among industrial goods has been recorded, with the greatest share for the overall increase being contributed by garments and petroleum products.
However, a decline in earnings was reported in the categories of printing industry products and plastics products. Export of garments to all major markets (US, the European Union, and UK) improved.
Earnings from the export of petroleum products improved due to the increase in both prices and volumes of bunker and aviation fuel exports.
Agricultural exports: Total earnings from the exports of agricultural goods in April 2022 increased by 7.3%, compared to April 2021. This increase was mainly attributed to exports of coconut products (mainly, coconut fibre, coconut oil and desiccated coconut), minor agricultural products (mainly, areca nuts, sesame seeds and plants and parts of plants) and seafood.
Export earnings from tea in April 2022 increased marginally by 1.5% YoY mainly driven by the increase in volumes amidst low prices.
Meanwhile, earnings from unmanufactured tobacco, spices (mainly, pepper and cloves) and vegetables, recorded decreases in April 2022.
Mineral exports: Earnings from mineral exports in April 2022 nearly halved compared to April 2021, mainly due to a decline in export earnings from titanium ores categorised under ores, slag, and ash.
Export indices: The export volume index and unit value index increased by 5.9% and 11.2% YoY respectively in April 2022, indicating that the increase in export earnings can be attributed mainly to the higher export prices.
Merchandise trade balance and terms of trade
Trade Balance: The trade deficit recorded a month-on-month decline for the fourth consecutive month in April 2022, supported by the policy measures that were aimed at discouraging non-urgent imports.
The deficit in the trade account narrowed to $ 729 million in April, compared to the deficit of $ 889 million in April 2021.
However, the cumulative deficit in the trade account during the first four months widened to $ 3.13 billion from $ 2.94 billion recorded in the same period a year earlier.
Terms of trade: Terms of trade i.e. the ratio of the price of exports to the price of imports, deteriorated by 6.3% in March 2021 as the increase in import prices were higher than the increase of export prices, compared to March 2020.