Friday Mar 28, 2025
Friday Mar 28, 2025
Tuesday, 18 April 2017 00:30 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
Digitally-developed economies around the globe are continuing to progress due to larger investments and adoptions in Information Communication Technology. At the same time, digitally-developing economies have also started to accelerate their growth by 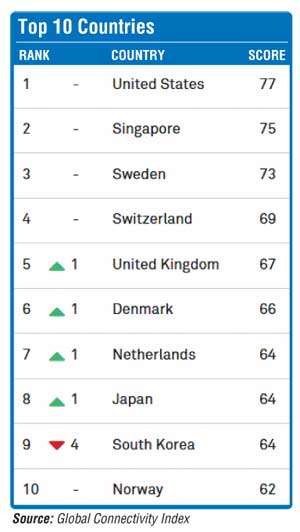 investing strategically in ICT capabilities and their digital transformation journeys – yet the gap continues to grow.
investing strategically in ICT capabilities and their digital transformation journeys – yet the gap continues to grow.
Those are some of the findings in the just announced Huawei Global Connectivity Index (GCI) 2017, the fourth annual study that shows how countries are progressing with digital transformation based on 40 unique indicators that cover five technology enablers: broadband, data centres, cloud, big data and Internet of Things. Investing in these five key technologies enables countries to digitise their economies. Through centralised planning, potential connectivity can be fully leveraged and ICT capabilities can support positive growth of national economies.
According to GCI 2017, global progress towards a digital economy is picking up pace. The world’s GCI score is up four percentage points since 2015. The report shows that ICT has become an engine of economic growth.
Of the 50 countries that were analyzed, 16 are considered Frontrunners, 21 are Adopters, while the remaining 13 are Starters. These clusters reflect the nations’ progress in digital transformation. Frontrunners (average GDP per capita of $ 50,000) are mostly developed economies, continually boosting digital user experience, using big data and IoT to develop more intelligent, efficient societies. Adopters (average GDP per capita of $15,000) are focused on increasing ICT demand to facilitate industry digitisation and high-quality economic growth. Starters (average GDP capita of $3,000) are in the early stage of ICT infrastructure build-out, and focus on increasing ICT supply to give more people access to the digital world.
The report said economic planners should give priority attention to widening inequality, noting “the digital divide becomes a digital chasm”. “By examining three years of GCI data, we see growing inequality, an ICT version of the ‘Matthew Effect’ – the sociology theory that states: ‘the rich get richer and the poor get poorer’. [This] suggests, groups or individuals that have an accumulated advantage over time not only succeed, but leverage their initial advantage to pull farther and farther ahead of competitors. Policy makers need to understand that this widening digital divide will impact every sector of the economy and society. Nations that cannot build sustainable economic growth may also have difficulty in feeding, educating and providing job opportunities for their people,” the report said.
Frontrunners achieved an increase of 4.7 GCI points from 2015 to 2017 by leveraging the capabilities of Cloud, Big Data and IoT. Adopters experienced a lift of 4.5 points on average. The slower Starters fell farther behind in their ability to compete in the Digital Economy, with only a 2.4 point improvement in overall GCI scores.
Key areas where inequality between the clusters is an issue include mobile broadband subscriptions, IT workforce per capita, ICT investment per GDP, apps download per capita and IoT installed base per capita. It should be noted that a 1 point increase in GCI score is equivalent to 1) a 2.1% increase in competitiveness 2) 2.2% increase in national innovation, and 3) a 2.3% increase in productivity.
GCI 2017 study reported the relationship between ICT investment and GDP growth is generally accepted in government and industry. Examining the GCI 2017 data with numerous economic forecasting models, the report said a nation which increased investment in ICT investment in infrastructure by additional 10% annually from 2017 to 2025 can benefit from a multiplier effect. “Using this economic impact model we find that every additional $1 of ICT infrastructure investment could bring a return of $3 in GDP at present, $3.70 in 2020 and the potential return increases to $5 in 2025,” the report said.
“The widening gap has had a significant impact on countries as they develop and work their way toward digital transformation,” said Kevin Zhang, President of Huawei Corporate Marketing. “To stay competitive, nations at an early stage of digital transformation will need to prioritise ICT infrastructure development, especially broadband connectivity and cloud adoption to a strategic level in economic planning to activate local resources and reach sustainable growth. At the same time, nations aiming to capitalise on their Frontrunner status will want to prioritise cloud as a potent catalyst to initiate a chain reaction of transformation through big data and IoT.”
The 50 countries assessed by the GCI 2017 account for 90% of global GDP and 78% of the world’s population.
For more information about the Huawei Global Connectivity Index 2017, visit: http://www.huawei.com/minisite/gci/en/.