Thursday Feb 26, 2026
Thursday Feb 26, 2026
Wednesday, 10 April 2019 01:02 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}

By Harsha Udayakantha Peiris
“Over 2,000 years ago, diligent and courageous people of Eurasia explored several routes of trade and cultural exchanges that linked the major civilisations of Asia, Europe and Africa. We see that there existed three silk routes in the history, says Duan Tao, Dean Academy of Commerce of Yunnan Province, China.
These three silk roads were namely, the Southern Silk Road, Northern Silk Road and the Maritime Silk Road. The Southern Silk Road consisted of western line, middle line and eastern line. The ‘Shu-to-Yuandu’ road of this Southern Silk Road started from Chengdu in Sichuan, through Yunnan to Myanmar, India and further to central and Western Asia as well as the Mediterranean region in Europe. The Northern Silk Road was an important carrier of exchanges and interactions between ancient northwestern China and Central, Southern and Western Asia as well as Europe and Africa. The Maritime Silk Road connected ancient China to other regions in the world, including two major lines of ‘East China Sea Shipping Line’ and ‘South China Sea Shipping Line’.
 |
Chinese President Xi Jinping speaking at the opening ceremony of ‘The Belt and Road’ Forum for International Cooperation in May 2017 |
 |
Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe inspects the port of Hambantota during his recent visit to Weerawila, Hambantota |
“For thousands of years, the spirit, peace and cooperation, open-mindedness, mutual learning and mutual benefit of the Silk Road sparked legend,” Tao says.
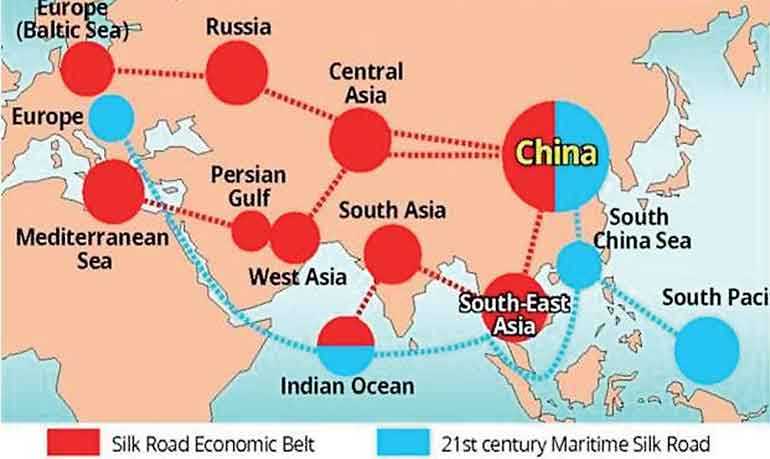
Chinese President Xi Jinping raised the initiative of jointly building the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road during his visit to Central and South Eastern Asia countries in September and October of 2013.
In May 2017 at the Opening Ceremony of ‘The Belt and Road’ Forum for International Cooperation Xi Jinping – President of the People’s Republic of China stated that the recent years had seen increased trade connectivity and China had worked with other countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative to promote trade and investment facilitation and improve business environment.
Total trade between China and other Belt and Road countries in 2014-2016 has exceeded $ 3 trillion. The Chinese President also stated that China’s investment in these countries had surpassed $ 50 billion and Chinese companies had set up 56 economic cooperation zones in over 20 countries, generating some $ 1.1 billion of tax revenue and 180,000 jobs for them.
China’s economy is highly correlated with world economy as China will stick to a consistent path of the basic state policy of opening to the outside world with the construction of fully opened and a new pattern of deepening integration to the world’s economic system.
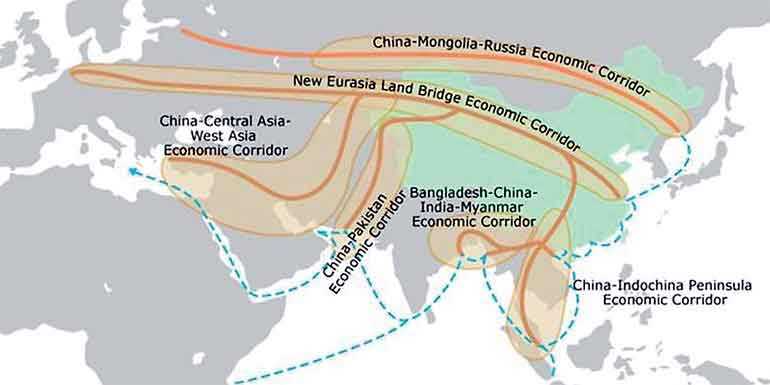
Under such comprehensive course of socio-economic development, China’s ‘Belt and Road’ initiative has introduced six economic corridors spanning Asia, Europe and Africa namely, China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor, New Eurasia Land Bridge Economic Corridor, China-Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor, China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar Economic Corridor and China-Indochina Peninsula Economic Corridor. Connecting to network amongst these six corridors will be implemented through open, inclusive, mutually beneficial and joint operation mechanisms.
According to the Academy of Commerce of Yunnan Province and Yunnan International Trade Association, the great significance of jointly building the Belt and Road Initiative is expected to provide new power for the world economy, optimise and innovate the international cooperation and global governance mechanism, promote to build an all-round open and a new pattern and Promote the Afro Eurasian regional development and peace and development of mankind.
The principles of jointly building the initiative hence include to abide by the purposes and principles of the UN charter, be open for cooperation, be harmonious and inclusive, follow market operation and seek mutual benefits and win-win results.
Through the ideas of peace and cooperation, openness and being inclusive, mutual learning and mutual benefit by means of promoting practical cooperation in all fields, creating mutual political trust, economic integration and culture inclusiveness, the goal towards the framework for the development of the Belt and Road Initiative is to build a community of shared interests and responsibility.
Policy coordination, connectivity of facilities, unimpeded trade, financing integration and people-to-people bond have been set as cooperation priorities of the initiative. Strengthening bilateral cooperation, carrying out multi-level and multi-channel communications and negotiations and promoting all-round development of bilateral relations have been clearly depicted as cooperation mechanisms.
The establishment of Silk Road Fund has provided a direct driving force for the construction of Belt and Road Initiative. China has invested USD 40 billion to establish the Silk Road Fund. Through this fund Countries along ‘the Belt And the Road’ will be benefitted with infrastructure connectivity, industrial investment, resources development, economic and trade cooperation, financial cooperation, cultural exchange, ecological protection and maritime cooperation All investment and financing support to the projects are related to mutual connectivity.
By 15 April 2015, 57 countries have had the intention of being the founding members of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), which was a highly welcome idea in the Belt and Road project including 37 countries within the region, and 20 outside the region. Members covered all five continents.
China’s foreign capacity cooperation under ‘Belt and Road’
According to Prof. Zhu Li of YNUFE School of Business Management the capacity Cooperation Opportunity between China and Developing Countries include characteristics, current situation and problems of economic development of developing countries, instability of economic development, single industrial structure dominated by agriculture, serious shortage in infrastructure construction, low industrialisation and urbanisation level and high pressure in poverty reduction and labour quality and skills to be improved without delay.
Meanwhile, significance for Promoting International Capacity Cooperation under Belt and Road Initiative include deepening economic and trade cooperation level between countries, boosting complementarity of industrial advantages and industrial coordinated development of regions and countries, promoting the building of regional value chain and improve industrial competitiveness of regions and countries and boosting the cultivation of leading industry of every country concerned.
At the May 2017 forum, Chinese President Xi Jinping also stressed that industries were the foundation of economy, and the country should deepen industrial cooperation so that industrial development plans of different countries would complement and reinforce each other. “Focus should be put on launching major projects. We should strengthen international cooperation on production capacity and equipment manufacturing, and seize new development opportunities presented by the new industrial revolution to foster new businesses and maintain dynamic growth,” he pointed out.
Accordingly, the thought and key points of international capacity cooperation are to boost coordinated development of industries of the countries along the economic corridor, cultivate competitive and leading industry of each country concerned, enhance industrial competitiveness, build regional value chain, gradually form regional production network structure, boost free and reasonable flow of regional production factors to realise advantage complementarity of resource, technology, capital and market.
Lancang-Mekong countries
Taking Lancang-Mekong countries as examples, interesting elements are learned on the basis and conditions for developing international capacity cooperation under Belt and Road Initiative as economy of Lancang-Mekong countries is growing rapidly and continuously. In recent years, economic growth rate of these ASEAN countries has exceeded 5% averagely.
According to World Bank reports, from 2011 to 2015, average growth rate of Laos’ GDP reached up to 7.4% and GDP per capita increased from $ 319 to $ 1970. In 2014, the average GDP growth rate of Vietnam reached 6%, Malaysia 6% and Myanmar 7.7%. The interconnection and interworking pattern of Lancang-Mekong countries is basically formed through China-Vietnam, China-Laos-Thailand (Kunming-Bangkok Expressway), China-Myanmar expressways, direct flights from China to all Lancang-Mekong countries to strengthen aviation transport, Yunnan-Vietnam railway and China-Laos railway which is under construction and strengthening sea transport.
Via the system guarantee for capacity cooperation with Lancang-Mekong countries, upgrading of China-Asean Free Trade Zone is under construction for Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). Building of Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is pushed forward steadily and regional cooperation under Lancang-Mekong cooperation mechanism tends to be closer.
With Lancang-Mekong element of the Belt and Road Initiative, all countries that include are speeding up the development of regional economic integration and amalgamation of economic development. Economic vitality of those countries, abundant labour resources, Resource endowments with different characteristics have been identified as advantages for Lancang-Mekong countries whilst mature industry technology, abundant capitals and huge domestic market have been identified as advantages for China under conjunction points for cooperation with Lancang-Mekong countries. The main understanding is that development of regional economic integration promotes the full integration of industry, capital and market factors.
Sino-Nepal Friendship Industrial Zone
Lhasa Economic and Technological Development Zone Investment and Development Co., Ltd., Nepal Industrial Zone Management Co., Ltd. and China Ping An Trust Co., Ltd. signed the Framework Cooperation Agreement of Sino-Nepal Friendship Industrial Zone successfully at the parallel theme meeting ‘Policy Communication and Development Strategy Docking’ of ‘The Belt and Road’ Forum for International Cooperation in the afternoon May 14, 2017.
The planned investment for the project is $ 1 billion and that for Phase One is $ 0.5 billion for the development and construction of industrial zone within Nepal which mainly introduces international and domestic energy industries, consumer goods manufacturing, vehicle assembly such as automobile and motorcycle, water purification treatment, processing of agricultural and animal products, electronic products, new energy industry and other entity production enterprises, with the aim to meet the local needs, build economic industry chain for South Asia, form industrial competitive advantages, continuously develop South Asia markets and improve industrial development level towards benefits of characteristic industries of Nepal and Tibet.
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, the Colombo Port City and Hambantota Port
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor and the Colombo Port City of Sri Lanka are also key initiatives in this regard to boost partnership on International capacity cooperation fields. Building capacity cooperation platforms such as international economic cooperation zones, international industrial parks and cross-border economic cooperation zones are several major concerns. It is imperative that governments of all countries concerned give guarantee with respect to cooperation policy and cooperative mechanism through international investment, transnational corporation, international trade and other ways. Strengthening cooperation in key industrial fields is another major emphasis.
China possesses a large quantity of competitive industries and abundant high-quality capacity as well as highly cost-effective equipment and products and thus can help all countries concerned to improve industrialisation level through capacity cooperation. Cooperation in such fields as infrastructure, engineering machinery, electrical energy, building materials and communication will be strengthened in neighbouring economies in line with such strength to combine with resource endowments of all countries concerned and to strengthen the cultivation of leading industries thereof.
On 30 March Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe inspected the port of Hambantota, a major southern port operated by China Merchants and expressed confidence in the operation capacity of China Merchants Port, since its operation was taken over by the Hambantota International Port Group (HIPG). This emphasises a further appreciation of Sri Lanka’s contribution to shipping, economy, employment and social welfare.
The visit by the Prime Minister was the second inspection of the Hambantota area within a week of period, parallel to the Younpura 2019, a major youth program conducted at Weerawila in Hambantota District. Ren Rui, the Chief Representative of China Merchant Group in Sri Lanka and CEO of HIPG, reported to the Prime Minister and his delegation to explain the production and operation situation and future development plan since HIPG took over the Port of Hambantota.
Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone
Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone in Cambodia is another major investment under Belt and Road Initiative. Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone (SSEZ), is a national overseas economic and trade cooperation zone in Sihanoukville developed and constructed by HOdo Group with Chinese and Cambodia enterprises in 2008 with a total plan area of 11.13 square km.
As of 2017, SSEZ has introduced 109 enterprises (institutions) in total, 94 of which are Chinese-funded enterprises, and has become an important platform for Chinese-funded enterprises to enter Cambodia. It mainly involves textile and garment, hardware, machinery and electronics, suitcases and leather ware and other labour intensive industries.
These initiatives also focus to the point that international capacity cooperation should be based on the principle of ‘mutual benefit, complementation and coordination’ and preference should be given to the industries of bilateral mutual concerns that have strong conductive power for economic development of those countries and can boost the regional coordinated development. Here, capacity cooperation should aim at the overall improvement of industrial performance of target countries, rather than rests on industrial output unilaterally. Industrial structure and industrial development direction connect and combine with industries of all countries concerned to select industry for cooperation. With enterprises as main body and market as orientation, the cooperative targets are the perfection of industrial structure and industrial competitiveness of each country concerned.
Key points of capacity cooperation in this regard include, strengthening construction of interconnection and interworking. It also emphasises that interconnection and interworking is an important power to deepen regional cooperation, trade costs of regional economic cooperation should be reduced quickly and market space to be expanded and interconnection and interworking is the basis for building high-efficiency capacity cooperation to expand market space.
As of the end of 2016, Chinese enterprises had established about 56 overseas economic and trade cooperation zones within the countries along “the Belt and Road” with an accumulative investment of $ 18.55 billion and taxes paid to host countries of $ 1.07 billion, creating 177,000 jobs for the local people. It can be said that overseas economic and trade cooperation zone has become an important point for undertaking the construction of “the Belt and Road” and also a platform for Chinese enterprises to ‘go out.’
And according to Chinese President Xi Jinping at the opening ceremony of ‘The Belt and Road’ Forum for International Cooperation in May 2017, these fruitful outcomes show that the Belt and Road Initiative responds to the trend of the times, conforms to the law of development, and meets the people’s interests. It surely has broad prospects.