Tuesday Feb 24, 2026
Tuesday Feb 24, 2026
Thursday, 2 May 2024 03:39 - - {{hitsCtrl.values.hits}}
 Exports in March have risen to a 19-month of $ 1.14 billion propelling the first quarter performance by 5.7% to $ 3.17 billion, according to latest external trade data released by the Central Bank.
Exports in March have risen to a 19-month of $ 1.14 billion propelling the first quarter performance by 5.7% to $ 3.17 billion, according to latest external trade data released by the Central Bank.
Exports in March were the highest since the August 2022 figure of $ 1.22 billion, and 9.8% above the achievement in the corresponding month of last year and above February 2024 figure of $ 1.05 billion.
Expenditure on merchandise imports recorded an increase of 4% to $ 1.5 billion in March and by 13% to $ 4.4 billion in the 1Q.
The CBSL said the deficit in the merchandise trade account narrowed to $ 369 million in March 2024 from $ 412 million recorded in March last year, primarily due to a higher increase in exports than the increase in imports. However, it widened compared to February 2024 ($ 319 million).
The cumulative deficit in the trade account during January to March 2024 was higher ($ 1.22 billion) than the deficit recorded over the same period in 2023 ($ 896 million).
The robust external trade comes amidst Sri Lanka rupee appreciating by 9% against the US dollar during the year up to 30 April 2024.
Last year exports were down by 9% to $ 11.9 billion from $ 13.1 billion in 2022. The Central Bank envisages exports in 2024 to increase by 8.4% to $ 12.9 billion.
CBSL said increases in export earnings were seen across all major categories of exports, where industrial exports increased the most. The export volume index increased by 19.7%, while the unit value index declined by 8.3%, implying that the increase in export earnings in March 2024 compared to March 2023 can be attributed to higher export volumes.
The increase in industrial goods exports in March 2024 by 11.7% to $ 912.2 million was mainly contributed by petroleum products (up 134% to 92.3 million) due to the increase in volumes of bunkering and aviation fuel exports, while textiles and garments exports also recorded a notable improvement, up by 6.6% to 445 million. Earnings from exports of agricultural goods rose by 2.7% to $ 222 and mainly driven by tea (led by higher volumes) and coconut-related products, despite a significant decline in spice exports. Earnings from mineral exports increased marginally in March 2024.
The improvement in earnings from exports in March 2024 compared to February 2024 was largely driven by higher textiles and garments exports, which was the highest earnings from these exports recorded since December 2022.
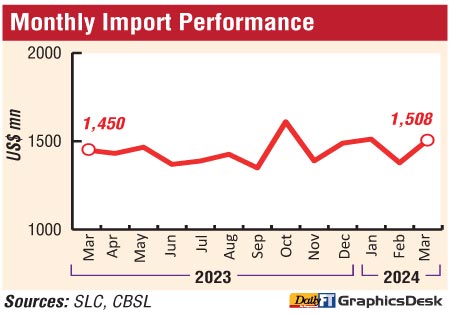 CBSL also said expenditure across all major import categories increased, although intermediate goods led by fuel imports increased the most. The increase in expenditure on consumer goods imports in March 2024 compared to a year ago was due to an increase in expenditure on food and beverages imports, although there was a decline in non-food consumer goods imports (led by lower medical and pharmaceuticals). Meanwhile, expenditure on intermediate goods imports increased primarily due to higher fuel imports compared to March 2023. However, expenditure on textiles and textile articles, wheat and fertiliser significantly decreased in March 2024. Expenditure on investment goods recorded a broad-based increase, driven primarily by higher imports of building materials and machinery and equipment. Meanwhile, expenditure on imports in March 2024 increased significantly compared to February 2024 primarily due to the normalisation of fuel expenditure.
CBSL also said expenditure across all major import categories increased, although intermediate goods led by fuel imports increased the most. The increase in expenditure on consumer goods imports in March 2024 compared to a year ago was due to an increase in expenditure on food and beverages imports, although there was a decline in non-food consumer goods imports (led by lower medical and pharmaceuticals). Meanwhile, expenditure on intermediate goods imports increased primarily due to higher fuel imports compared to March 2023. However, expenditure on textiles and textile articles, wheat and fertiliser significantly decreased in March 2024. Expenditure on investment goods recorded a broad-based increase, driven primarily by higher imports of building materials and machinery and equipment. Meanwhile, expenditure on imports in March 2024 increased significantly compared to February 2024 primarily due to the normalisation of fuel expenditure.
The import volume index improved by 17.3%, while the unit value index declined by 11.4%, implying that the increase in import expenditure in March 2024 compared to March 2023 was also driven by the volume effect.